Ablative lasers, such as CO2 and Er:YAG, may be regarded as superior to traditional surgical techniques – elliptical excision, curettage, cautery and cryotherapy – because they provide greater precision and uniformity in lesion removal. This enhanced accuracy translates into improved safety and a markedly reduced risk of sequelae, particularly scarring and pigmentary changes.
The Er:YAG laser (2940nm) is absorbed very efficiently by water, allowing for extremely precise ablation with minimal thermal injury. As a result, Er:YAG treatment is associated with faster healing and an even lower incidence of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation compared to the CO2 laser (10,600nm).
Patient selection and preparation
Any patient presenting with an epidermal lesion or superficial verrucous nevus may be considered for Er:YAG ablation once a definitive diagnosis has been established, preferably through histopathological examination. Accurate diagnosis is essential to rule out malignant or atypical lesions and to ensure that the treatment is both safe and appropriate.
A comprehensive medical history and dermatological evaluation should be performed prior to the procedure. Patients with active local infections, photo-aggravated skin diseases, bleeding disorders or a known history of keloid or hypertrophic scarring are generally unsuitable candidates. Other contraindications include pregnancy, certain autoimmune or connective tissue disorders and concurrent use of photosensitising medications, which may increase the risk of adverse cutaneous reactions.

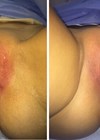
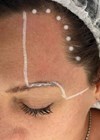
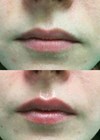
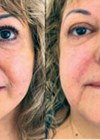
Figure 1: Before (left) and after (right).

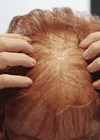
Figure 2: Before (left) and after (right).
Procedure
Before the first laser procedure, a small excisional biopsy followed by histopathological analysis was performed, confirming the diagnosis of verrucous epidermal nevus. The treatment area is thoroughly cleansed prior to the procedure and topical or local anesthesia is used to ensure patient comfort. All equipment in our setup includes the SP Dynamis (Fotona, Slovenia), the R11 handpiece (configured with a 2mm spot size) and the Pen1.0D handpiece (with a fixed 1mm spot size).
To minimise excessive heat deposition, shorter pulse modes such as MSP or SP are employed. A 2mm spot size is generally used for thicker or larger nevi, allowing efficient ablation of bulkier tissue. In contrast, a 1mm spot size is preferred for smaller lesions, where greater precision is required.
The fluence range is typically set between 5–12 J/cm². Lower fluence values provide finer precision but require more time to achieve the desired effect, while higher fluence values enable faster removal, particularly for larger or more robust lesions.
A similar principle applies to frequency settings, which are usually adjusted between 5–10Hz. Lower firing rates (around 5Hz) allow for more controlled and precise work, whereas higher frequencies (up to 10Hz) increase speed and efficiency when treating larger areas.
A wet gauze is applied throughout the treatment area to gently remove debris and ablated tissue, ensuring a clean field and optimal visibility during the procedure.
Post-treatment care and recovery
For the treatment case presented, a topical antibiotic ointment was applied and the treated area was covered with plasters immediately after the procedure. For home care, the patient was instructed to use a re‑epithelialisation cream (such as Bepanthen, Aquaphor or a similar product) several times daily for approximately one week, or until the scabs had fully resolved.
Strenuous physical activity was discouraged during the initial healing period. Soaking in water (e.g. sauna, baths, swimming pools) was not recommended in the first few days, although showering was permitted.
In this case, the entire lesion was ablated over three sessions. This approach was chosen due to the difficulty of achieving complete infiltrative anesthesia across the area of the verrucous nevus. Furthermore, given that the patient was a 15‑year‑old boy, we sought to minimise postoperative discomfort and facilitate a more tolerable recovery.
Assessing results and follow-up
With careful, precise execution and attentive aftercare, Er:YAG ablation provides a safe and effective method for the complete removal of epidermal lesions, resulting in excellent cosmetic outcomes and highly satisfied patients.
Declaration of competing interests: Anže Zorman is employed by Fotona to teach and lecture about Fotona treatments and is also involved in clinical research.